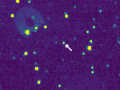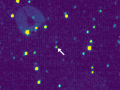
English: In April 2016, NASA's New Horizons spacecraft observed 1994 JR1, a 90-mile (145-kilometer) wide Kuiper Belt object (KBO) orbiting more than 3 billion miles (5 billion kilometers) from the sun, for the second time. Taken with the spacecraft's Long Range Reconnaissance Imager (LORRI) on April 7-8 from a distance of about 69 million miles (111 million kilometers), the images shatter New Horizons' own record for the closest-ever views of this KBO in November 2015, when New Horizons detected JR1 from 170 million miles (280 million kilometers) away.
Combining the November 2015 and April 2016 observations allows scientists to pinpoint the location of JR1 to within 1,000 kilometers (about 600 miles), far better than any small KBO. The more accurate orbit also allows the science team to dispel a theory that JR1 is a quasi-satellite of Pluto.
From the closer vantage point of the April 2016 observations, the team also determined the object's rotation period, observing the changes in light reflected from JR1's surface to determine that it rotates once every 5.4 hours (or a JR1 day).
The observations are great practice for possible close-up looks at about 20 more ancient Kuiper Belt objects that may come in the next few years, should NASA approve an extended mission. New Horizons flew through the Pluto system on July 14, 2015, making the first close-up observations of Pluto and its family of five moons. The spacecraft is on course for an ultra-close flyby of another Kuiper Belt object, 2014 MU69, on Jan. 1, 2019.
Above, the first two of the 20 observations that New Horizons made of 1994 JR1 in April 2016. The Kuiper Belt object is the bright moving dot indicated by the arrow. The dots that do not move are background stars. The moving features in the top left and far right are internal camera reflections (a kind of selfie) caused by illumination by a very bright star just outside of LORRI's field of view; the one on the left shows the three arms that hold up LORRI's secondary mirror.